Source https://c1.staticflickr.com/4/3867/15100973910_c696db8853_b.jpg
Concentrations of CO2 in the Earth’s atmosphere surged to a record high in 2016, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
Last year’s increase was 50% higher than the average of the past 10 years.
Researchers say a combination of human activities and the El Niño weather phenomenon drove CO2 to a level not seen in 800,000 years.
Scientists say this risks making global temperature targets largely unattainable.
This year’s greenhouse gas bulletin produced by the WMO is based on measurements taken in 51 countries. Research stations dotted around the globe measure concentrations of warming gases including carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide.
The figures published by the WMO are what’s left in the atmosphere after significant amounts are absorbed by the Earth’s “sinks”, which include the oceans and the biosphere.
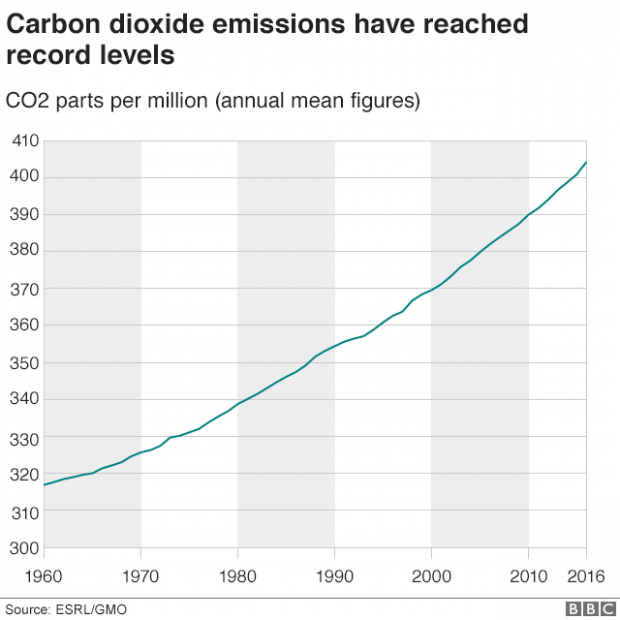
A brief history of Earth’s CO2
2016 saw average concentrations of CO2 hit 403.3 parts per million, up from 400ppm in 2015.
“It is the largest increase we have ever seen in the 30 years we have had this network,” Dr Oksana Tarasova, chief of WMO’s global atmosphere watch programme, told BBC News.
“The largest increase was in the previous El Niño, in 1997-1998, and it was 2.7ppm; and now it is 3.3ppm. It is also 50% higher than the average of the last 10 years.”
El Niño impacts the amount of carbon in the atmosphere by causing droughts that limit the uptake of CO2 by plants and trees.
Emissions from human sources have slowed down in the last couple of yearsaccording to research, but according to Dr Tarasova, it is the cumulative total in the atmosphere that really matters as CO2 stays aloft and active for centuries.
Over the past 70 years, says the report, the increase in CO2 in the atmosphere is nearly 100 times larger than it was at the end of the last ice age.
Rapidly increasing atmospheric levels of CO2 and other gases have the potential, according to the study, to “initiate unpredictable changes in the climate system… leading to severe ecological and economic disruptions”.
The study notes that since 1990 there has been a 40% increase in total radiative forcing. That’s the warming effect on our climate of all greenhouse gases.
“Geological-wise, it is like an injection of a huge amount of heat,” said Dr Tarasova.
“The changes will not take 10,000 years, like they used to take before; they will happen fast. We don’t have the knowledge of the system in this state; that is a bit worrisome!”
According to experts, the last time the Earth experienced a comparable concentration of CO2 was three to five million years ago, in the mid-Pliocene Epoch. The climate then was 2-3C warmer, and sea levels were 10-20m higher due to the melting of Greenland and the West Antarctic ice sheets.
Other experts in the field of atmospheric research agreed that the WMO findings were a cause for concern.
“The 3ppm CO2 growth rate in 2015 and 2016 is extreme – double the growth rate in the 1990-2000 decade,” Prof Euan Nisbet from Royal Holloway University of London, UK, told BBC News.
“It is urgent that we follow the Paris agreement and switch rapidly away from fossil fuels. There are signs this is beginning to happen, but so far the air is not yet recording the change.”
Another concern in the report is the continuing, mysterious rise of methane levels in the atmosphere, which were also larger than the average over the past 10 years. Prof Nisbet says there is a fear of a vicious cycle, where methane drives up temperatures which in turn releases more methane from natural sources.
“The rapid increase in methane since 2007, especially in 2014, 2015, and 2016, is different. This was not expected in the Paris agreement. Methane growth is strongest in the tropics and sub-tropics. The carbon isotopes in the methane show that growth is not being driven by fossil fuels. We do not understand why methane is rising. It may be a climate change feedback. It is very worrying.”
The implications of these new atmospheric measurements for the targets agreed under the Paris climate pact are quite negative, say observers.
“The numbers don’t lie. We are still emitting far too much and this needs to be reversed,” said Erik Solheim, head of UN Environment.
“We have many of the solutions already to address this challenge. What we need now is global political will and a new sense of urgency.”
The report has been issued just a week ahead of the next instalment of UN climate talks, in Bonn. Despite the declaration by President Trump that he intends to take the US out of the deal, negotiators meeting in Germany will be aiming to advance and clarify the rulebook of the Paris agreement.
30 October 2017
Matt McGrath
This article was originally published on BBC-News. Read the original article.





